Integrity is an international consultancy and service provider working in challenging and complex environments around the world. We offer integrated research, monitoring, evaluation and learning services to support evidence-based programming in such contexts. The organization has offices in DC, London, Amman, and Nairobi and has delivered over 200 projects for government clients including USAID, State Department, the UK Department for International Development (DFID), and the UK Foreign Commonwealth Office. Integrity’s Data and Knowledge Management (DKM) team leads the development and use of digital solutions in the organization’s work, from the use of readily available tools to custom-built platforms and applications.
In the use of technology solutions in our work, Integrity follows the Principles for Digital Development and a Do No Harm approach, especially important in fragile and conflict-affected environments. As we have seen, when deployed intelligently and ethically, technology can play a significant role supporting evidence-based approaches in development programming.
Aqoonta: A Digital Solution for Third Party Monitoring in Somalia
Integrity leads a consortium to implement DFID’s Learning and Monitoring Program – Somalia (LAMPS, 2016-2020), delivering third-party monitoring and partner M&E capacity assessments to DFID’s Somalia Monitoring Program (SMP II). The LAMPS program verifies DFID Somalia’s Governance, Health, and Economic Development portfolios to improve DFID’s understanding of how the activities it funds are performing, the challenges faced, and as a means to identify, mitigate and learn from risks affecting programming. DFID requested the development of a digital platform to augment LAMPS processes to capture, aggregate, and enable analyses of verification results. Integrity and partners developed Aqoonta (Somali for “knowledge”) – a web-based platform where DFID and partners can access and interact with concise, visual LAMPS reports, photographs, management dashboards and learning resources. Aqoonta is a vehicle through which DFID and its implementing partners can learn from and improve their delivery.
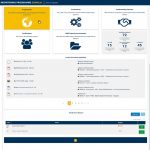 The platform has more than 250 active users and catalyzes learning and action by improving the quality and availability of information and its dissemination through intelligent, automated user notifications. Each report produced in Aqoonta enables DFID and partners to engage on findings, risks, and lessons learned from verifications. The platform improves the quality and availability of information DFID has at its disposal when making decisions on its Somalia programs. The LAMPS team worked with DFID’s Digital Spend Team throughout the development of Aqoonta, and the platform features as a case study on DFID’s internal digital learning portal (‘Digital Grid’).
The platform has more than 250 active users and catalyzes learning and action by improving the quality and availability of information and its dissemination through intelligent, automated user notifications. Each report produced in Aqoonta enables DFID and partners to engage on findings, risks, and lessons learned from verifications. The platform improves the quality and availability of information DFID has at its disposal when making decisions on its Somalia programs. The LAMPS team worked with DFID’s Digital Spend Team throughout the development of Aqoonta, and the platform features as a case study on DFID’s internal digital learning portal (‘Digital Grid’).
Integrity learned the following lessons developing Aqoonta:
- Commissioners of digital solutions benefit from investing in the design process – Integrity worked closely with LAMPS representatives to gather user needs for Aqoonta within DFID’s Somalia Country Office. Despite the limited capacity of busy staff to contribute to design, the team was able to assess activity and gather iterative rounds of user feedback throughout Aqoonta’s development through harvesting usage analytics and user comments within the platform.
- Digital platform development should only begin once workstreams are established and with appropriate time and resource for prototyping and testing – Before developing dashboards and analytical functions, it is critical to ensure clarity of the structure of reports and the reporting processes the platform will support. Allowing time for prototyping, testing and gathering user perspectives allowed for iterative digital developments.
- A digital solution should adapt to evolving program strategy and/or methodology –Aqoonta was developed using an agile software development methodology where requirements evolved through collaborative efforts. This was essential to achieve balance between flexibility and clear direction to meet objectives and enable adaptability, particularly in a constantly shifting operating environment like Somalia.
- Identifying and training digital platform champions ensures users have multiple routes to support– Integrity and partners worked to build capacity with Aqoonta ‘champions’ who serve as the first point of contact for users with problems accessing Aqoonta. DFID’s ‘champions’ enable the LAMPS team to absorb informal feedback from users and quickly identify and resolve minor issues that may otherwise reduce user engagement.
In our work and through Aqoonta, Integrity has first-hand experience of how technologies play a critical role supporting monitoring, evaluation, research, and learning for programs in fragile and conflict-affected environments. They are most effective in such contexts when anchored in a strong understanding of the context and operating environment, close relationships with the users of the service, and in retaining the flexibility to adapt ways of working to achieve objectives in rapidly-changing programs.

OTHER STORIES






